Top of the pageActionset
Skin Cancer: Preventing It and Watching for Early Signs
Overview
Excessive exposure to the sun and its ultraviolet (UV) rays can cause skin cancer. You can lower your risk for skin cancer by:
- Protecting your skin, and that of your family members, from UV radiation.
- Doing regular skin self-examinations.
- Finding out whether you have an increased risk for melanoma and other skin cancers.
How can you protect your skin from UV radiation and skin cancer?
Preventing skin cancer
Preventing skin cancer isn't always possible. But you can take steps to protect your skin from UV radiation. Sunscreen plays an important role in protecting your skin from UV radiation. But it can't prevent skin damage if you are exposed to the sun's rays for long periods of time. Experts recommend that you use more than one method to fully protect your skin.
- Stay out of the sun during the peak hours of UV radiation.
Peak hours are from 10 a.m. to 4 p.m. Find shade if you need to be outdoors. You can also find how much UV exposure you are getting by using the shadow rule. If your shadow is longer than you, then UV exposure is low. If your shadow is shorter than you, then UV exposure is high.
- Wear protective clothing.
This can include:
- Wide-brimmed hats that protect the face and neck.
- Tightly-woven clothes made of thick material, such as unbleached cotton, polyester, wool, or silk.
- Dark clothes with dyes added that help absorb UV radiation.
- Loose-fitting long-sleeved clothes that cover as much of the skin as possible.
- Clothes with sun protection factor (SPF) in the fabric that doesn't wash out.
- Wear sunscreen, with an SPF of 30 or higher, every day.
This includes summer and winter, on both cloudy and clear days.
- Use sunscreen that blocks both UVA and UVB radiation.
Apply to all exposed skin, including the nose, lips, ears, scalp, back of the hands, and neck. Apply sunscreen 30 minutes before going in the sun. Reapply it every 2 hours and after swimming, exercising, or sweating.
- Use protective lip balm.
Use lip balm or cream that has an SPF of 30 or higher to protect your lips from getting sunburned.
- Wear wraparound sunglasses.
Choose ones that block at least 99% of UVA and UVB radiation.
- Be careful when you are on sand, snow, or water.
These surfaces can reflect 85% of the sun's rays. Also be careful when you're at high elevations or in countries near the equator.
- Avoid artificial sources of UVA radiation.
This includes sunlamps and tanning booths. Like the sun, they can cause skin damage and increase the risk of skin cancer.
A child's skin is more sensitive to the sun than an adult's skin and is more easily burned. Babies younger than 6 months should always be completely shielded from the sun. Children 6 months and older should have their skin protected from too much sun.
Watching for early signs of skin cancer
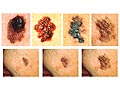
Skin cancer, including melanoma, is curable if spotted early. A careful skin exam may identify suspicious growths that may be cancer or growths that may develop into skin cancer (precancers).
- Learn the ABCDEs of early detection.
These are the changes in a mole or skin growth that are warning signs of melanoma.
-
Examine your skin regularly.
Get to know your moles and birthmarks. And look for any abnormal skin growth and any change in the color, shape, size, or appearance of a skin growth.
- Check for any area of skin that does not heal after an injury.
- Ask your doctor to check your skin during health exams.
Most experts recommend having your skin examined regularly.
- Bring any suspicious skin growths or changes in a mole to the attention of your doctor.
Credits
Current as of: December 4, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: December 4, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.