Basal and squamous cell carcinoma
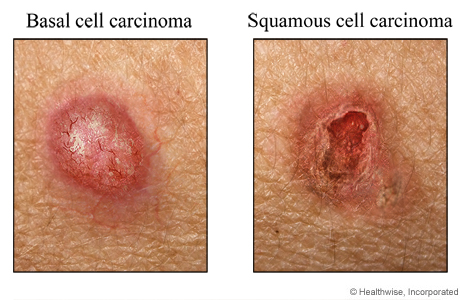
Basal cell carcinoma usually affects the face, head, and trunk of the body. The nose is the most common site. Signs of basal cell carcinoma can include skin changes such as a:
- Firm, pearly bump with tiny blood vessels that look spidery (telangiectasias).
- Red, tender, flat spot that bleeds easily.
- Small, fleshy bump with a smooth, pearly appearance, often with a lower area in the center.
- Bump that can be darker than the rest of your skin. This is more common in people with darker skin.
- Smooth, shiny bump that may look like a mole or cyst.
- Patch of skin, especially on the face, that looks like a scar and is firm to the touch.
- Bump or sore that itches, bleeds, crusts over, and then repeats the cycle and has not healed in a few weeks.
- Change in the size, shape, or color of a mole or a skin growth.
Squamous cell carcinoma often affects the head, neck, trunk, arms, and legs. But it can be any place on the body where there is skin. This includes inside the mouth, on the genitals, and near the anus. Signs of squamous cell carcinoma include any:
- Firm bump that does not go away. It is often on sun-exposed skin.
- Patch of skin that feels scaly, bleeds, or develops a crust. The patch may get bigger over a period of months and form a sore.
- Skin growth that looks like a wart.
- Sore that does not heal. It may appear in a scar or on skin that has ongoing problems.
- An area of thickened skin on the lower lip, especially if you smoke or use chewing tobacco or your lips are often exposed to the sun and wind.
Current as of: October 25, 2024
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.

